Weekly AI Venture Ecosystem Overview
#093@SVTR.AI
This week’s AI venture ecosystem displays several notable trends:
Overall funding remains robust, with new startups emerging rapidly in both application and model layers.
Founders’ educational backgrounds and work experience are diverse, yet top universities and major tech companies continue to dominate the AI startup scene.
Leading investment firms remain highly active, allocating significant capital to both early-stage and growth-stage ventures.
A number of AI-focused public companies have shown new developments in their financial and valuation metrics.
Below is a detailed breakdown from multiple perspectives.
I. Financing Overview
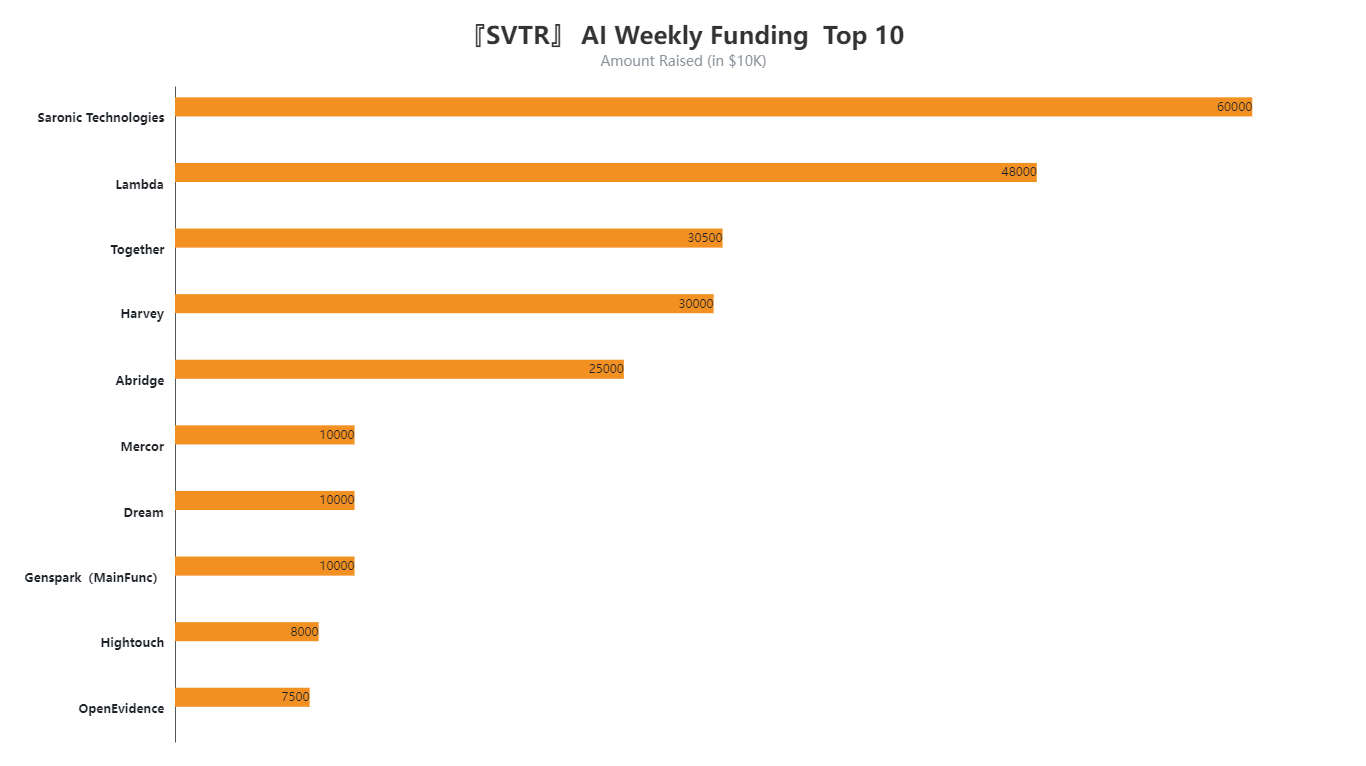
From the “AI Weekly Funding Top 10” list, we see that several companies have secured substantial funding, underscoring investors’ continued enthusiasm for AI startups. Notably:
Saronic Technologies tops the list with around $60 million (the chart shows 6000, where the unit is “ten-thousands of USD”).
Lambda follows with approximately $48 million.
Together and Harvey have raised about $30.5 million and $30 million, respectively.
Abridge is at $25 million.
Close behind are Messor and Genspark (Mankind), each raising around $10 million, Hightouch at $8 million, and OpenEvidence at $7.5 million.
These companies span diverse areas—ranging from general-purpose large language models and industry-specific applications to cloud infrastructure optimization—highlighting the continued rapid iteration and expansion across the AI landscape.
II. Application Ecosystem and Sector Distribution
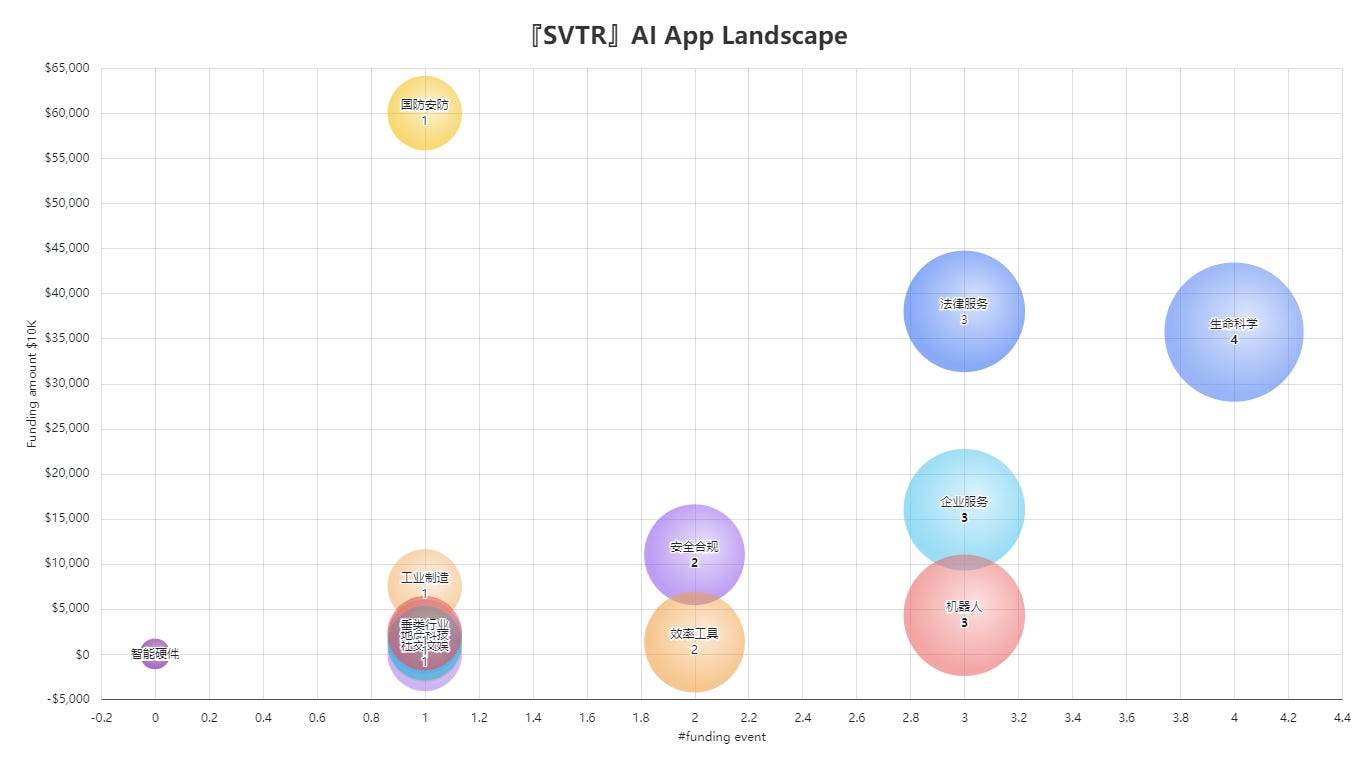
The “[SVTR] AI App Landscape” bubble chart provides a clear view of how various application-focused startups are positioned in terms of number of funding events (x-axis) and market size or user growth (y-axis). Notable observations include:
Companies developing large language model (LLM) applications (e.g., enterprise chatbots, intelligent customer service, content generation) have gained significant market traction and completed multiple funding rounds.
Some vertical industry solutions (e.g., healthcare AI, financial AI) are still in earlier stages of funding but demonstrate strong market potential due to their focus on specific industry pain points.
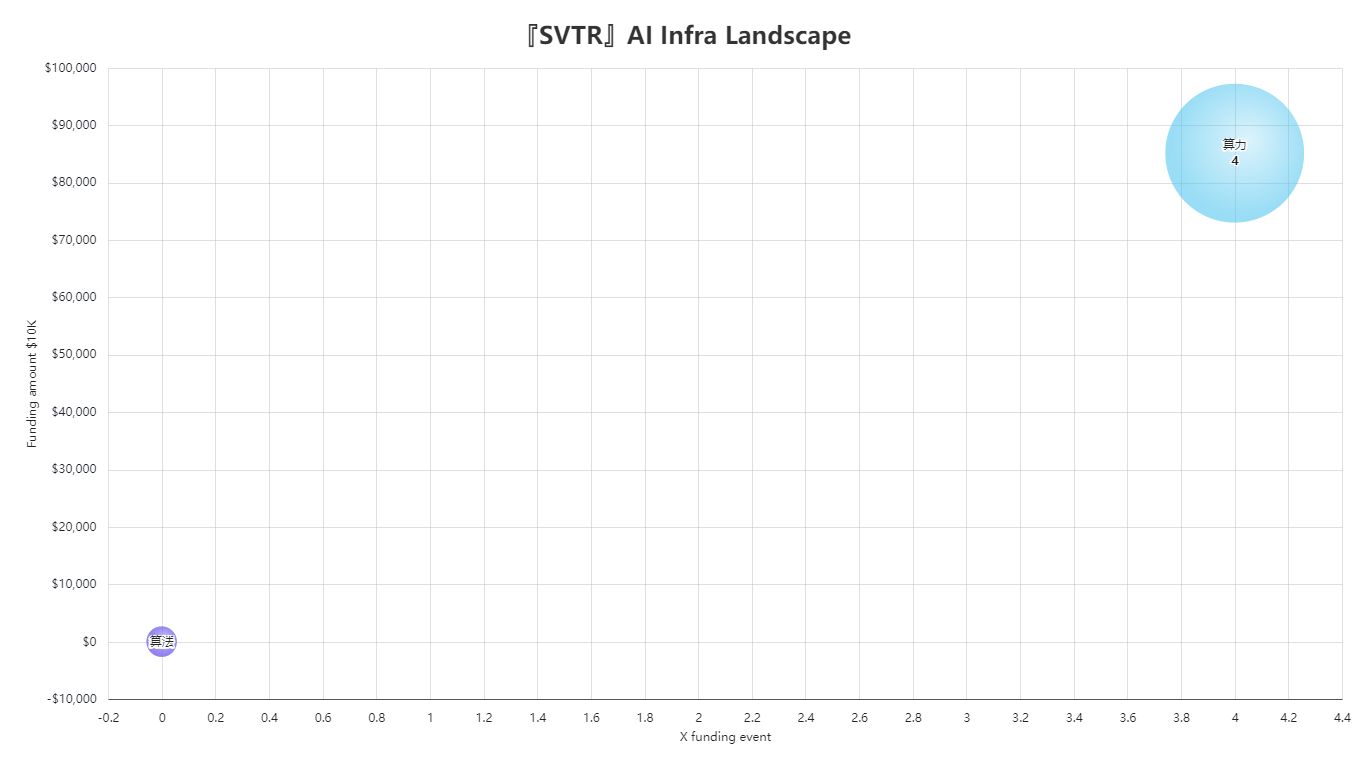
Meanwhile, the “[SVTR] AI Infra Landscape” chart shows how AI infrastructure startups are evolving. While certain projects focused on training platforms or inference chips have secured large funding rounds, the total number of deals remains relatively small, suggesting higher barriers to entry and more concentrated competition in the infrastructure space.
III. Founder Background and Talent Flow
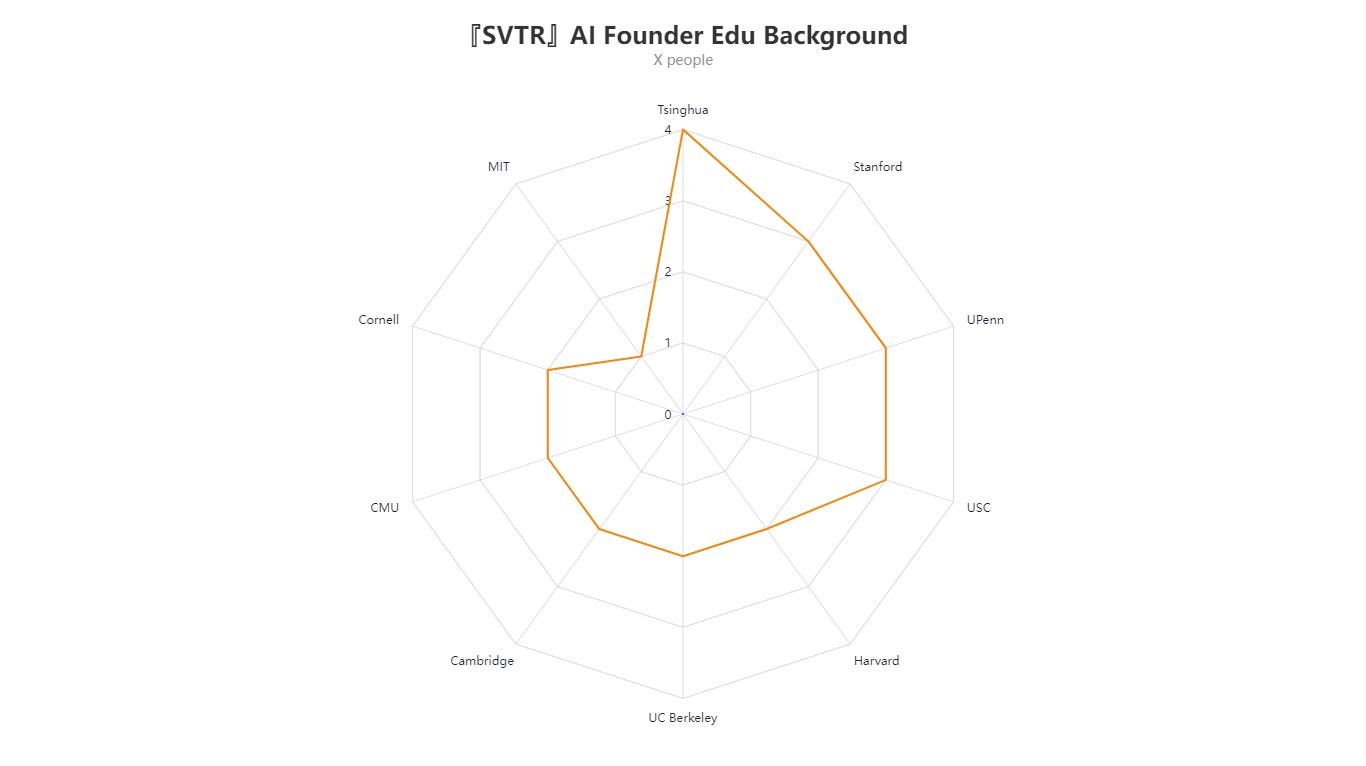
Educational Background
The “AI Founder Edu Background” radar chart indicates that this week’s tracked founders primarily hail from:
Tsinghua University and Stanford University, each with 4 founders,
University of Pennsylvania (UPenn) and University of Southern California (USC), each with 3,
Harvard University, UC Berkeley, and Cambridge University, each with 2,
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), Cornell University, and MIT, each with 1.
This distribution demonstrates that top universities—both in China and the U.S.—continue to play a significant role in nurturing AI startup founders.
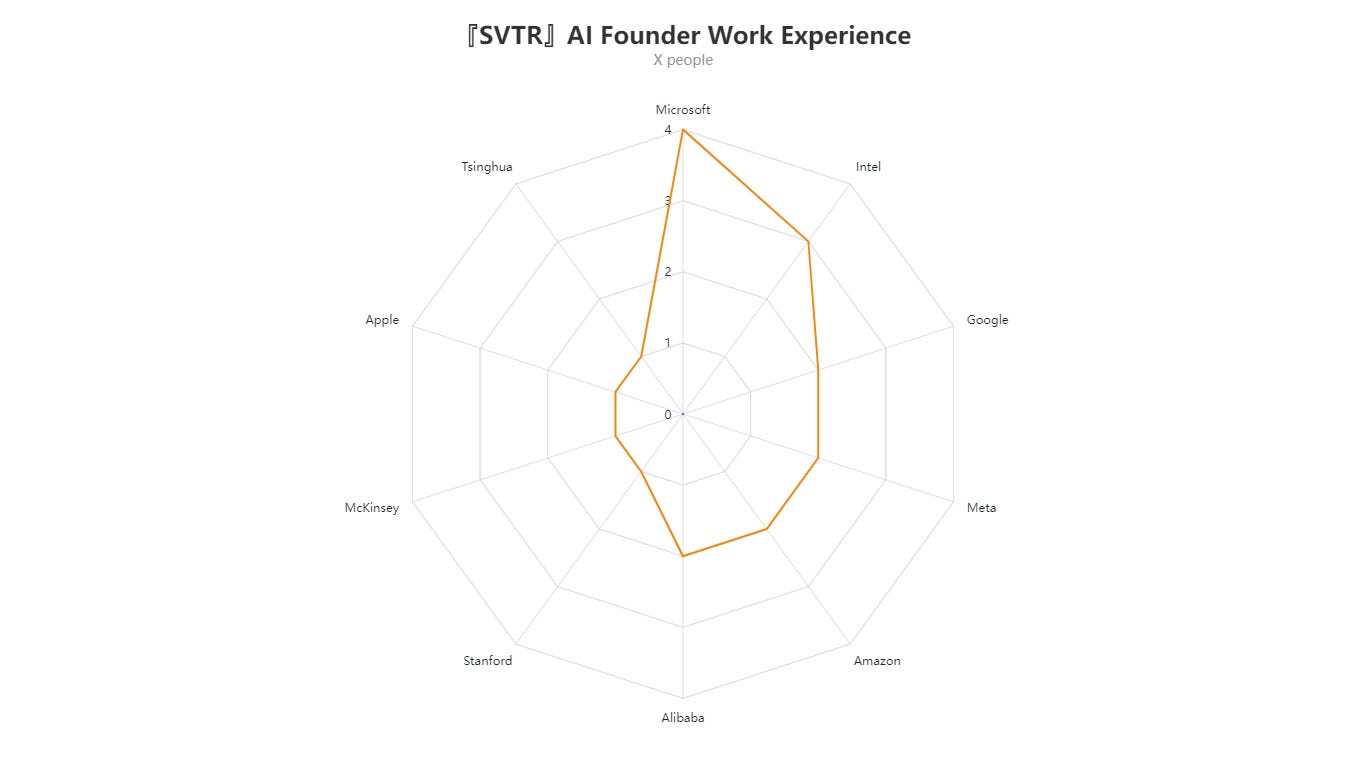
Work Experience
The “AI Founder Work Experience” radar chart shows that founders’ previous employers are concentrated among major tech giants, including Microsoft, Intel, Google, Meta, Amazon, and Alibaba. Microsoft stands out with 4 founders, followed by Intel and Google with 3 each, illustrating how big-tech backgrounds remain common in early-stage AI startups.
This trend suggests that experience in leading technology companies or frontline research institutions often provides the technical and managerial foundation that appeals to both capital and industry resources in the AI sector.
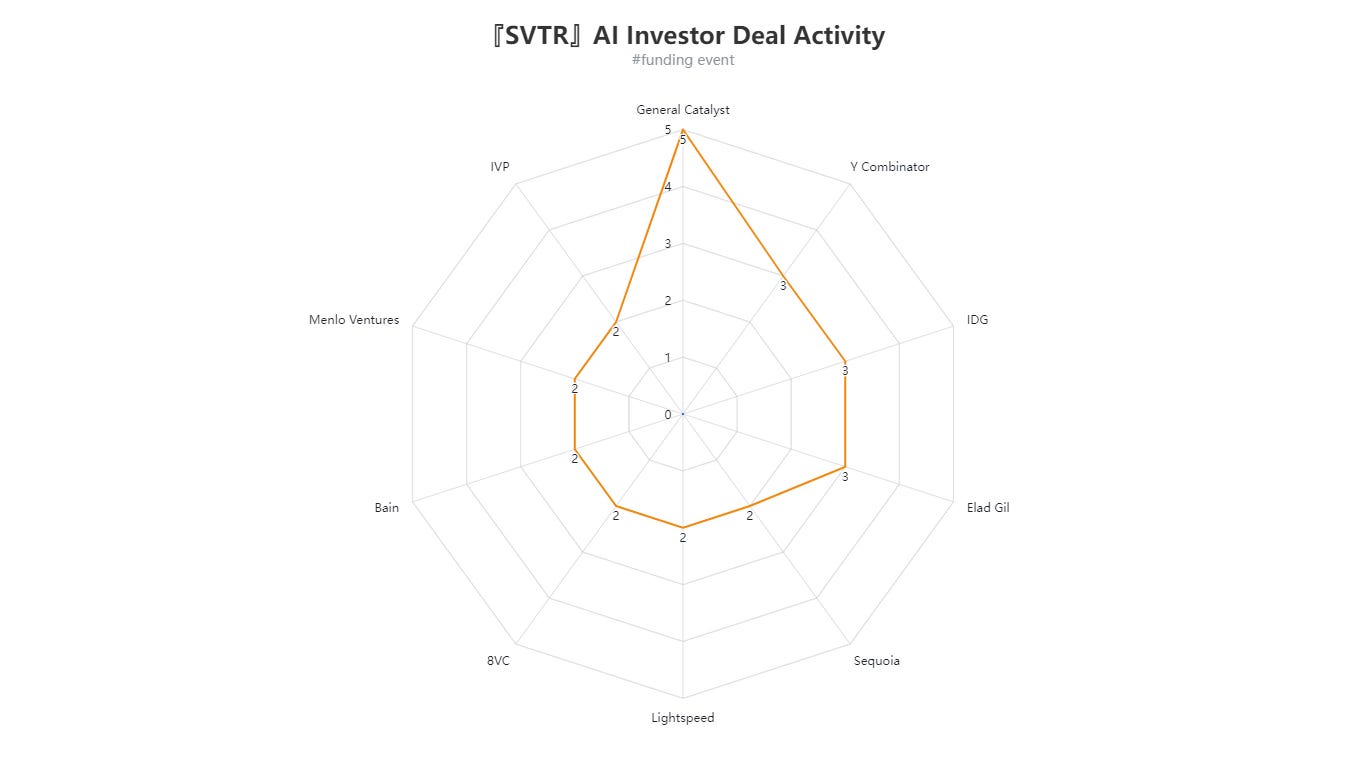
IV. Investor Trends
The “AI Investor Deal Activity” radar chart highlights several firms’ investment activity this week:
General Catalyst leads with 5 deals,
Y Combinator follows with 4 deals,
IDG and Edd Gil each have 3 deals,
Lightspeed, BVC, Bain, Menlo Ventures, and IVP are each around 2 deals.
These are all prominent international funds or notable angel investors, reflecting their ongoing bullishness on AI, particularly in large models, vertical applications, and infrastructure.
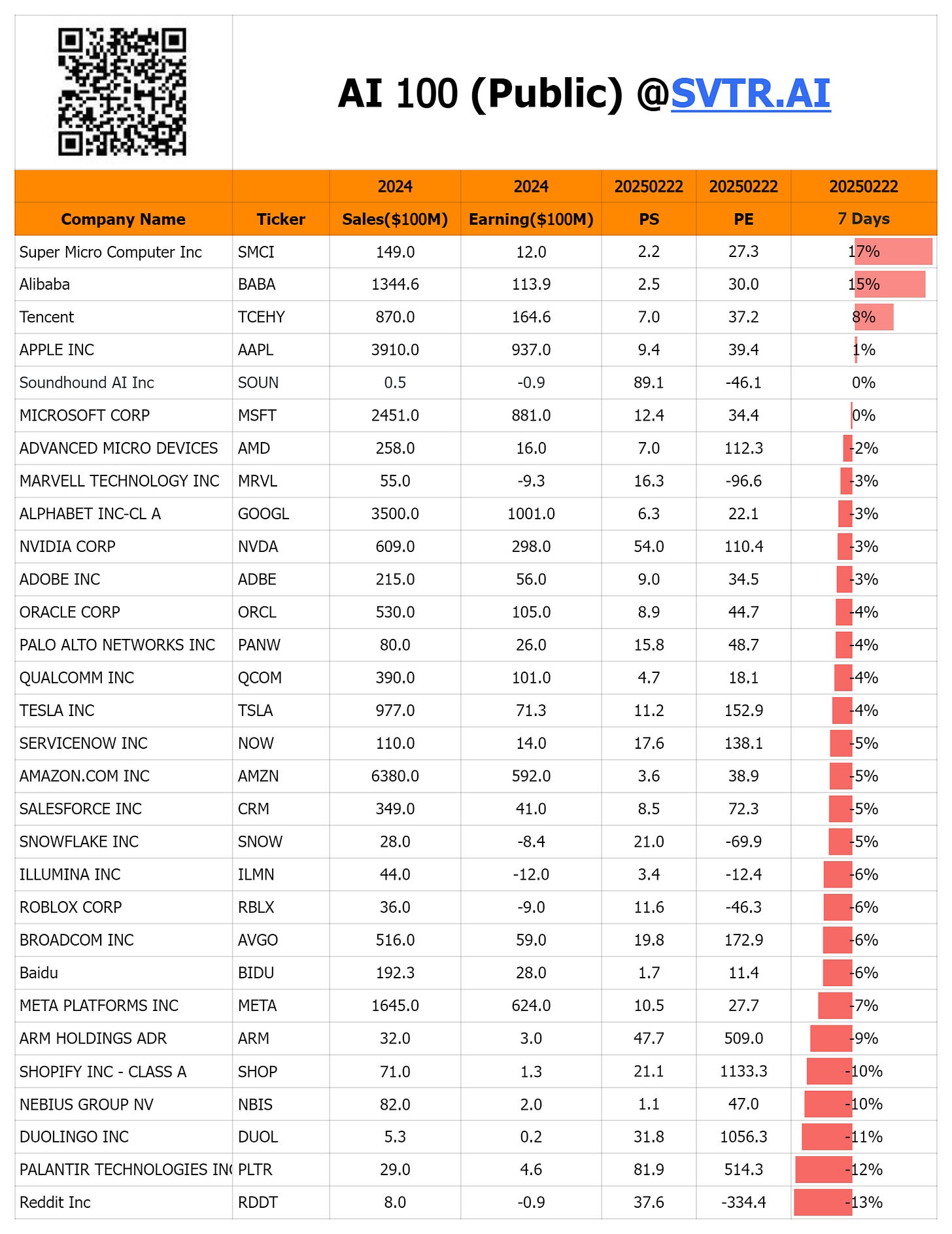
V. Public AI Companies
The “AI 100 (Public) @SVTR.AI” table provides insight into the financials and valuation metrics of key AI-related public companies, including sales, earnings, P/E ratios, and recent 7-day price movements. For example:
Super Micro Computer Inc (SMCI) is projected to have $8.1 billion in 2024 sales and $220 million in earnings, with a roughly 2.2% increase in the past 7 days.
Alibaba, Microsoft, NVIDIA, AMD, and other leading tech players are also on the list, each showing varying P/E ratios and stock price changes, reflecting the market’s combined view of their AI outlook and overall tech sentiment.
Overall, while many AI-linked public companies continue to perform strongly, broader macroeconomic factors and volatility in the tech sector have led to some short-term fluctuations.
VI. Conclusion and Outlook
In summary, this week’s AI venture ecosystem highlights the following:
Sizable Funding Rounds Continue: Companies such as Saronic Technologies, Lambda, and Together have attracted large-scale financing, demonstrating the sector’s rapid growth and sustained investor interest.
Multiple Tracks Advancing: Application-layer ventures focusing on large language models and vertical industries receive considerable attention, while foundational infrastructure and core model development also see increased investment.
Diverse Yet Major-Tech-Dominated Talent: Founders from Tsinghua, Stanford, Microsoft, and Google underscore the value of elite academic and corporate backgrounds.
Active Investor Participation: General Catalyst, Y Combinator, and other major funds have made multiple deals, reflecting confidence in AI’s long-term potential.
Mixed Public Market Performance: Some AI-related stocks maintain growth, but overall valuations remain subject to broader market forces and tech-sector adjustments.
As large model technology matures further, we expect continued emergence of new ventures and opportunities in enterprise services, industry-specific solutions, and AI infrastructure. For entrepreneurs, strong technical expertise, rapid product iteration, and keen insight into market needs will be critical to success. For investors, identifying projects with true competitive moats and scalable potential amid the ongoing AI boom remains both the greatest challenge and opportunity.